When an electric current flows through a wire there is a drop in voltage due to the resistance of the wire. The voltage drop is found from Ohm’s Law: E=IR, or Voltage Drop = Wire Resistance x Amps of Current.
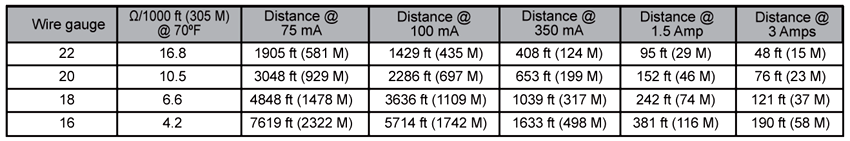
The wire length recommendations below represent a 10% voltage drop in a 24 VAC or VDC circuit for various wire gauges and maximum currents. The voltage drop is linear, therefore cutting the wire length in half would result in a 5% voltage drop rather than a 10% voltage drop. The currents in the two tables represent the various models of power supplies and voltage converters available from BAPI.
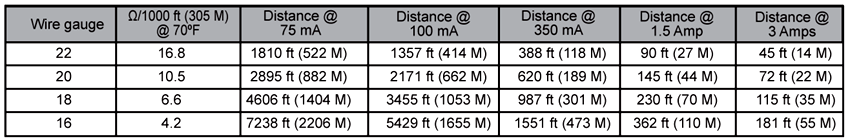
Wire length recommendations in Table 1 are based on a wire temperature of 70 ºF. If the wire is run in a portion of the building where temperatures can increase to 140 ºF, such as an unventilated attic, then decrease the recommended wire length by 5%, as shown in Table 2.
The minimum wire gauge is determined by the maximum worst-case load. When in doubt, use the next larger size wire. All wiring must comply with the National Electric Code (NEC) and local codes.
If you have any additional questions about wire lengths, please contact your BAPI representative.



